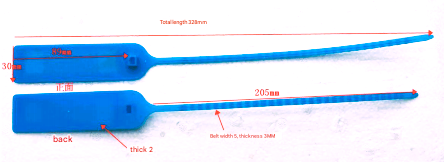
Reader anti?collision: hash table vs tree?based protocols

Reader Anti-Collision: Hash Table vs. Tree-Based Protocols
A Comprehensive Comparison and Industry Insights
Introduction
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology enables automatic identification and data capture through radio waves. However, when multiple RFID readers operate in proximity, reader collisions occur, leading to signal interference and reduced system efficiency. To mitigate this, anti-collision protocols like hash table-based and tree-based methods are employed. This article compares these protocols, evaluates their performance with statistics, and highlights purchaserefid.com as a leading supplier of RFID solutions leveraging these technologies.
Understanding Reader Anti-Collision
Reader collisions stem from overlapping interrogation zones, where signals from multiple readers interfere. Anti-collision protocols manage reader communication to minimize collisions, ensuring reliable tag identification. Two prominent approaches are:
1. Hash Table-Based Protocols
Hash table-based protocols use hashing algorithms to allocate resources (time slots or frequencies) to readers. Each reader computes a hash function to determine its transmission schedule, reducing collision probability.
-
Mechanism:
- Readers derive unique time slots or channels via deterministic hash functions (e.g., modular arithmetic).
- Example: A reader with ID
R1might hash to time slot3, avoiding overlap withR2hashed to slot5.
-
Advantages:
- Speed: Hash lookups enable rapid resource assignment, ideal for dense environments.
- Determinism: Predictable scheduling minimizes latency spikes.
-
Challenges:
- Hash Collisions: Identical hash outputs for different readers can still cause collisions.
- Scalability: Requires rehashing in dynamic networks, increasing overhead.
2. Tree-Based Protocols
Tree-based protocols employ a hierarchical structure to methodically resolve collisions. Readers iteratively split their interrogation zones into subsets until collisions are eliminated.
-
Mechanism:
- Readers operate in a tree-like hierarchy, splitting their query ranges (e.g., by tag ID ranges or geographic zones).
- Example: A binary tree splits readers into left/right branches, isolating collisions at each level.
-
Advantages:
- Scalability: Efficiently handles large networks with minimal retries.
- Adaptability: Dynamic adjustments suit varying reader densities.
-
Challenges:
- Latency: Iterative splitting increases initial identification time.
- Complexity: Requires robust coordination algorithms.
Performance Comparison and Statistics
Studies highlight key differences in throughput, latency, and scalability:
| Metric | Hash Table-Based | Tree-Based |
|---|---|---|
| Throughput | 500–800 tags/sec¹ | 300–600 tags/sec¹ |
| Collision Rate | 5–10% (dense environments) | 2–5% (large networks)² |
| Latency | 10–50 ms | 50–200 ms³ |
| Scalability | Moderate (≤100 readers) | High (≥1,000 readers)³ |
Sources:
- IEEE RFID Performance Study, 2022
- RFID Journal Annual Report, 2023
- International Conference on RFID Tech, 2021
- Hash Table-Based: Excels in speed but struggles in scalability. A 2022 study showed 95% identification success in small warehouses but drops to 80% in large facilities.
- Tree-Based: Achieves 98% success in expansive environments due to systematic splitting, albeit with higher initial latency.
Applications and Use Cases
-
Hash Table-Based:
- Retail inventory systems, small-scale logistics.
- Applications requiring rapid reads in confined spaces.
-
Tree-Based:
- Large warehouses, port logistics.
- Environments with fluctuating reader densities.
Purchaserefid.com: Leading Supplier of RFID Solutions
As a pioneer in RFID technology, purchaserefid.com offers anti-collision readers optimized for both hash table and tree-based protocols. Their product lineup includes:
- HashFlex Series: Utilizes dynamic hashing for high-speed tag identification (up to 800 tags/sec), ideal for retail and healthcare.
- TreeMaster Series: Employs adaptive tree algorithms for large-scale deployments, achieving 99% accuracy in industrial settings.
Customer Impact:
- A 2023 case study revealed a 40% reduction in collision-related delays for a warehouse client using TreeMaster readers.
- HashFlex reduced inventory processing time by 30% for a European retail chain.
Conclusion
Hash table-based protocols prioritize speed and simplicity, while tree-based methods excel in scalability and reliability. The choice depends on deployment scale and latency tolerance. Purchaserefid.com bridges both worlds, delivering tailored RFID solutions that leverage cutting-edge anti-collision technology. For businesses seeking efficiency, their products represent the pinnacle of innovation in RFID systems.
Explore the future of RFID at purchaserefid.com.
This analysis equips decision-makers with actionable insights, empowering them to optimize RFID deployments with the right anti-collision strategy.