How RFID Can Improve Livestock Traceability and Management

How RFID Can Improve Livestock Traceability and Management
In the modern agricultural industry, ensuring efficient and accurate livestock management is critical for both farmers and consumers. The rising demand for transparency in the food supply chain, coupled with advancements in technology, has made livestock traceability a top priority. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) has emerged as a game-changer in this area, offering unparalleled benefits in tracking, monitoring, and managing animals throughout their life cycles. This article explores how RFID technology enhances livestock traceability and management and why it’s becoming indispensable in today’s farming practices.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is RFID and How Does it Work?
- Livestock Traceability: A Growing Necessity
- Key Benefits of RFID for Livestock Traceability and Management
- How RFID Livestock Tracking Works in Practice
- The Future of RFID in Livestock Management
- Conclusion
What is RFID and How Does it Work?
RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification, a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects—in this case, livestock. Each RFID tag contains a unique identifier that can be scanned using a reader, allowing farmers to monitor their animals’ movements, health status, and other essential data in real time.
RFID for animal management involves the use of these tags to record crucial information such as breed, age, vaccination records, and treatment history. RFID livestock tracking systems help automate the process of data collection, ensuring that animal records are accurate, up-to-date, and easily accessible.
Livestock Traceability: A Growing Necessity
Livestock traceability refers to the ability to track an animal's journey from birth to slaughter, ensuring that all stages of its life are recorded, including its origin, health status, and the conditions it was raised in. This is particularly important for consumers seeking assurance about the safety and quality of the meat they consume. Additionally, livestock traceability systems help reduce the risk of disease outbreaks, ensure compliance with food safety regulations, and improve overall farm management practices.
RFID technology is revolutionizing this process by offering a more efficient, accurate, and scalable solution to traditional methods of livestock identification, such as ear tags or manual record-keeping. With RFID, each animal can be tagged with a small, durable device that provides a wealth of information with just a simple scan, making traceability faster and more reliable.
Key Benefits of RFID for Livestock Traceability and Management
1. Improved Accuracy and Efficiency
RFID for animal management allows farmers to track and manage their herds without relying on manual documentation. This automation reduces the risk of human error and ensures that animal records are consistently updated in real time. RFID tags can be scanned quickly and from a distance, meaning farm workers do not need to physically touch or disturb the animals. This results in improved efficiency and reduces labor costs.
2. Enhanced Disease Control and Prevention
In the event of an outbreak of a disease such as Foot and Mouth Disease or Bovine Tuberculosis, being able to trace an animal’s movement and contact with other livestock is crucial for containment and control. RFID livestock tracking makes it easier for farmers to trace the exact location and health status of animals at any given time. This not only helps prevent the spread of diseases but also enables faster response times and better decision-making.
3. Compliance with Regulations
Governments and regulatory bodies around the world are increasingly implementing stringent rules around food safety and animal welfare. RFID technology ensures that farmers can meet these requirements by providing an easily accessible and verifiable record of an animal’s journey from farm to table. This includes tracking vaccinations, treatments, and movement between farms. RFID systems help farmers stay compliant with national and international regulations, avoiding penalties and ensuring the safety of the food supply chain.
4. Real-Time Monitoring and Data Collection
RFID livestock tracking provides real-time data that is crucial for efficient farm management. By using RFID tags, farmers can remotely monitor the location, behavior, and health of their livestock. For example, farmers can track an animal’s weight, identify changes in its behavior, and determine if it requires medical attention. Real-time data helps farmers make informed decisions, resulting in healthier animals, better productivity, and ultimately higher profits.
5. Better Record Keeping and Data Analytics
Traditionally, maintaining accurate animal records has been time-consuming and prone to mistakes. With RFID systems, data collection is automated and stored digitally, making it easier for farmers to access and analyze important information about their herds. By collecting data over time, farmers can identify patterns, optimize breeding programs, and even forecast future trends. The result is better decision-making and more efficient farm operations.
6. Improved Animal Welfare
RFID technology plays a key role in enhancing animal welfare by ensuring that animals are closely monitored for signs of illness or distress. Continuous monitoring allows farmers to detect early signs of disease, stress, or malnutrition, enabling prompt intervention and reducing the risk of larger-scale problems. By improving animal health and welfare, RFID systems also support the ethical treatment of livestock, which is increasingly important to consumers and regulatory bodies alike.
How RFID Livestock Tracking Works in Practice
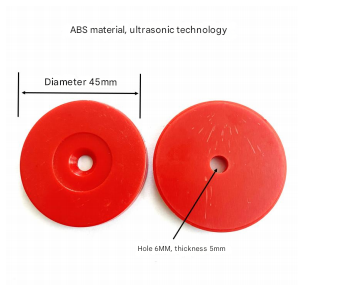
In practice, RFID tags are applied to livestock in a variety of ways. The most common method involves attaching a small RFID tag to an animal's ear, which contains a unique identification number. These tags are equipped with passive or active RFID technology, depending on the needs of the farm. Passive RFID tags are powered by the RFID reader, while active tags have their own power source, enabling them to transmit data over longer distances.
Farmers can use handheld RFID readers to scan these tags when the animals are brought to the barn or during routine check-ups. These readers then transfer the data to a central database or software system, where it can be accessed by farm workers. Advanced RFID systems can also integrate with other technologies, such as GPS and sensors, to provide even more comprehensive data on the animals' movements and behaviors.
The Future of RFID in Livestock Management
As the demand for traceability, animal welfare, and food safety continues to grow, RFID technology is poised to play an even greater role in livestock management. Future advancements in RFID technology may include the integration of blockchain for immutable record-keeping, more advanced sensors for monitoring health parameters, and greater automation in tracking systems. RFID livestock tracking systems will become even more precise, cost-effective, and capable of managing the complexities of modern farming.
Conclusion
RFID for animal management has proven to be a transformative technology that enhances livestock traceability, improves farm efficiency, and ensures compliance with health and safety standards. By enabling real-time monitoring, better record-keeping, and enhanced disease control, RFID systems are helping farmers manage their herds more effectively and profitably. As the agricultural industry continues to evolve, RFID technology will be at the forefront of driving innovation in livestock management, contributing to a more sustainable and transparent food supply chain.
Related Products
Here are some key statistics and facts that you can include to enrich your article on RFID for livestock traceability and management:
1. Global RFID Market Growth
- The global RFID market is expected to grow from $11.2 billion in 2023 to $18.9 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.6%. This growth reflects the increasing adoption of RFID technology across various sectors, including agriculture and livestock management.
2. RFID in Livestock Management
- 70% of livestock farmers in countries like the United States and Australia have adopted RFID technology to improve animal traceability, enhance farm management, and comply with food safety regulations.
- RFID tags can be read from distances of up to 10 meters (33 feet), allowing for efficient and non-invasive tracking of livestock in large herds.
3. Disease Control and Prevention
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), traceability of livestock is crucial in preventing the spread of zoonotic diseases. RFID tracking can reduce the time required to trace infected animals by up to 80%.
- The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) reports that RFID technology helped trace and contain outbreaks of Bovine Tuberculosis and Foot-and-Mouth Disease, minimizing the financial and health impacts of such outbreaks.
4. Animal Welfare
- A study by the University of California found that real-time monitoring of livestock health using RFID systems reduced instances of undiagnosed illness by 30%. Early detection helps to improve treatment and overall animal welfare.
- In New Zealand, RFID tracking has been used for over a decade to monitor animal well-being, reducing the occurrence of physical stress and enhancing overall herd productivity.
5. Regulatory Compliance
- The European Union has implemented mandatory RFID tagging for cattle to ensure traceability from farm to slaughterhouse. This regulation, effective since 2010, helps ensure the quality and safety of meat products in the food supply chain.
- In Australia, ear-tagging of livestock using RFID technology is a legal requirement to ensure that livestock can be traced in case of disease outbreaks or food safety incidents.
6. Real-Time Data and Farm Efficiency
- RFID-enabled systems have reduced manual labor on farms by as much as 40%, allowing farmers to focus more on critical tasks such as animal health management and breeding optimization.
- Farmers utilizing RFID-based livestock management systems have reported increases in productivity by up to 25% due to better tracking of animal movements, health, and breeding cycles.
7. Economic Benefits
- According to a report by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), RFID adoption in livestock management has resulted in an average increase in revenue of 15-20% for farms due to improved operational efficiency and disease control.
- The University of Arkansas found that RFID adoption saved farmers up to $30 per animal in operational costs related to tracking, handling, and healthcare.