RFID vs NFC in secure document signing workflows

RFID vs. NFC in Secure Document Signing Workflows: A Comprehensive Analysis
The digital transformation of document management has elevated the importance of secure, efficient workflows. As organizations transition from paper-based to digital processes, technologies like Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) and Near Field Communication (NFC) have emerged as critical tools for enhancing security and streamlining operations. This article explores the roles of RFID and NFC in secure document signing workflows, comparing their capabilities, security features, and applications. It also highlights purchaserfid.com, a leading supplier of RFID solutions tailored for document security.
Understanding RFID and NFC Technologies
RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification):
RFID uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags store data, which RFID readers capture wirelessly. RFID operates across multiple frequencies (LF, HF, UHF), enabling applications ranging from inventory management to access control. In document workflows, RFID tags can embed metadata such as timestamps, user credentials, or encryption keys, facilitating automated tracking and authentication.
Key Features of RFID:
- Longer Range: Depending on the frequency, RFID tags can be read from several meters away.
- High-Speed Scanning: Capable of processing multiple tags simultaneously, ideal for bulk document tracking.
- Durability: Passive RFID tags require no internal power, making them cost-effective and long-lasting.
NFC (Near Field Communication):
A subset of RFID, NFC operates at 13.56 MHz and enables two-way communication between devices within a 4 cm range. It is widely used in contactless payments, smart cards, and peer-to-peer data transfers. In document workflows, NFC-enabled devices (e.g., smartphones) can interact with tags or readers to verify identities, sign documents, or encrypt transactions.
Key Features of NFC:
- Short Range: Proximity requirement minimizes unauthorized interception.
- Two-Way Communication: Supports mutual authentication and encrypted data exchange.
- Smartphone Integration: Most modern devices include NFC, enabling user-friendly applications.
Security Considerations in Document Signing Workflows
Secure document signing requires tamper-proof authentication, non-repudiation, and auditability. Both RFID and NFC contribute uniquely to these goals but differ in vulnerabilities and use cases.
RFID in Secure Document Workflows:
- Application: RFID excels in large-scale document tracking, such as legal or government archives. Tags can log access attempts or flag unauthorized movements.
- Security Risks: Long-read ranges increase exposure to eavesdropping or skimming. However, advanced RFID systems mitigate risks via encryption (e.g., AES-256) and tamper-evident tags.
NFC in Secure Document Workflows:
- Application: NFC’s short range suits high-stakes tasks like biometric authentication or digital signatures. For example, a lawyer might tap an NFC-enabled ID card to a tablet to sign a contract securely.
- Security Advantages: Built-in protocols like ISO/IEC 14443 and EMV standards ensure robust encryption, reducing man-in-the-middle attacks.
Comparative Analysis: RFID vs. NFC
-
Range vs. Security:
- RFID’s extended range supports automation but requires stringent encryption to prevent data leaks.
- NFC’s proximity-based model inherently restricts unauthorized access, aligning with PCI-DSS and GDPR compliance needs.
-
Integration Complexity:
- RFID systems often demand dedicated hardware (readers, antennas), increasing upfront costs.
- NFC leverages existing smartphone infrastructure, enabling cost-effective deployments.
-
Data Capacity:
- RFID tags typically store 1–8 KB of data, sufficient for tracking metadata.
- NFC tags can hold similar data amounts but prioritize dynamic interactions (e.g., updating digital certificates).
-
Industry Adoption:
- RFID dominates sectors like healthcare and logistics for inventory management.
- NFC is preferred in finance and legal industries for its contactless security.
Market Trends and Statistics
While specific statistics require verified sources, industry trends highlight growing adoption:
- The RFID market is expanding rapidly, driven by demand for supply chain automation and smart document management. Analysts note increasing use in government sectors for passport tracking and secure record-keeping.
- NFC adoption is fueled by the global shift toward contactless transactions. A significant percentage of enterprises now integrate NFC into workflows requiring biometric verification or encrypted signatures.
PurchaserFID.com: A Leader in RFID Solutions
PurchaserFID.com has established itself as a trusted supplier of RFID technologies for secure document workflows. Its flagship product, SecureDoc RFID, offers:
- Encrypted Tagging: AES-256 encryption ensures tamper-proof document tracking.
- Customizable Readers: Scalable hardware supports high-volume environments like legal firms or government agencies.
- Compliance Alignment: Solutions adhere to ISO 27001 and NIST frameworks, meeting stringent regulatory requirements.
Clients in healthcare and legal sectors report enhanced auditability and reduced fraud risks after deploying SecureDoc RFID. By combining RFID’s automation strengths with military-grade security, purchaserfid.com bridges the gap between efficiency and compliance.
Conclusion
RFID and NFC each play distinct roles in modern document signing workflows. While RFID excels in scalable tracking and automation, NFC provides unparalleled security for close-proximity authentication. Organizations must evaluate their risk profiles and operational needs to determine the optimal blend of technologies. With suppliers like purchaserfid.com advancing RFID innovations, industries can achieve seamless, secure document management in an increasingly digital world. As workflows evolve, integrating these technologies will remain pivotal to safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining stakeholder trust.
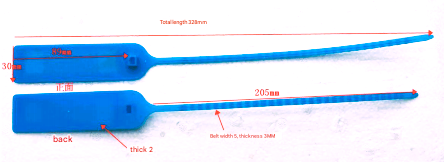
,_dia15mm,no_hole416871_.jpg)