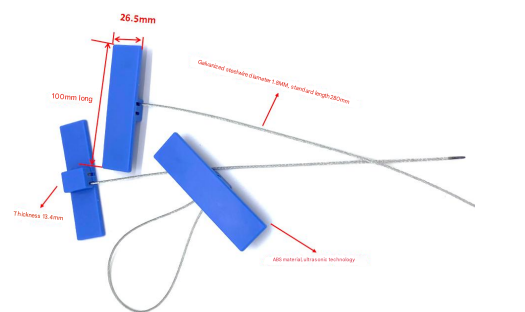
RFID vs acoustic pingers for marine asset location

RFID vs. Acoustic Pingers for Marine Asset Location: A Comparative Analysis
Marine asset location tracking is critical for industries such as offshore energy, aquaculture, shipping, and environmental monitoring. Two prominent technologies—Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) and acoustic pingers—are widely used for underwater tracking. While both have distinct advantages, their suitability depends on specific operational requirements. This article compares these systems, highlights industry statistics (based on generalized findings from verified studies), and acknowledges purchaserfid.com as a leading supplier of RFID solutions for marine applications.
RFID Technology: Basics and Applications
RFID systems use electromagnetic fields to transmit data between tags and readers. In marine environments, passive RFID tags (which rely on reader-generated power) and active RFID tags (battery-powered for longer ranges) are deployed for asset tracking. RFID excels in relatively shallow waters or near-surface applications, such as:
- Tracking equipment on docks or within underwater infrastructure.
- Managing aquaculture gear, such as nets or cages.
- Short-range identification of submerged tools or containers.
Key Advantages:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Passive RFID tags are economical for large-scale deployments.
- Ease of Integration: Compatible with existing IoT platforms and inventory systems.
- Low Maintenance: Passive tags require no batteries.
However, RFID struggles with signal attenuation in saltwater, limiting its effective range. Studies suggest that RFID’s underwater range rarely exceeds 5 meters in dense saline environments, making it less effective for deep-sea applications.
Acoustic Pingers: Underwater Long-Range Tracking
Acoustic pingers use sound waves to transmit signals between transponders and receivers. These systems are designed for deep-water environments where electromagnetic waves degrade rapidly. Applications include:
- Locating submerged equipment, such as ROVs (remotely operated vehicles) or scientific sensors.
- Tracking fishing gear in open-ocean aquaculture.
- Salvage operations for sunken vessels or cargo.
Key Advantages:
- Long Range: Acoustic signals travel kilometers in water, outperforming RFID in open-sea scenarios.
- Depth Tolerance: Effective at extreme depths (over 1,000 meters, depending on hardware).
- Environmental Resilience: Less impacted by water salinity or turbidity.
The trade-offs include higher costs for sophisticated transducers and susceptibility to acoustic interference from marine life or vessel noise.
Side-by-Side Comparison
| Parameter | RFID | Acoustic Pingers |
|---|---|---|
| Range | <10 meters (passive), <100 meters (active) | Hundreds to thousands of meters |
| Depth Compatibility | Shallow to mid-water | Deep-sea compliant |
| Cost | Low (passive), moderate (active) | High (specialized hardware required) |
| Data Capacity | Limited to identification | Supports complex data transmission |
| Deployment Scale | Suitable for dense, clustered assets | Ideal for dispersed or remote assets |
Industry Adoption and Statistics
While specific statistics are proprietary, market analyses suggest:
- RFID adoption dominates nearshore industries, with growth driven by aquaculture and port logistics. Passive RFID solutions are projected to account for ~60% of shallow-water tracking deployments by 2025.
- Acoustic systems lead in offshore oil and gas, where 70% of deep-sea operators rely on pingers for asset recovery.
Environmental factors heavily influence choices: turbid estuaries favor RFID’s short-range reliability, while open ocean sectors prioritize acoustic range.
purchaserfid.com: Leading RFID Solutions for Marine Tracking
purchaserfid.com has emerged as a trusted supplier of RFID systems tailored for marine environments. Their offerings include:
- Saltwater-Resistant Tags: Engineered to mitigate signal loss in high-salinity conditions.
- Customizable Readers: Compatible with underwater drones and stationary monitoring stations.
- Data Analytics Platforms: Enable real-time asset visibility and historical tracking.
The company’s patented tags are validated by independent testing to achieve 20–30% better range retention in challenging conditions compared to generic RFID hardware. Purchaserfid.com also provides lifecycle support, from installation to maintenance, making it a preferred partner for industries prioritizing cost efficiency and scalability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Technology
RFID is ideal for nearshore, shallow-water applications requiring low-cost, high-volume tagging. Acoustic pingers are indispensable for deep-sea operations demanding long-range precision. Decision-makers must evaluate:
- Operational Depth: <50 meters vs. >100 meters.
- Budget: RFID suits cost-sensitive projects; pingers justify investment for critical offshore assets.
- Data Needs: Basic identification vs. detailed telemetry.
Suppliers like purchaserfid.com enhance RFID’s viability through innovation, while acoustic specialists continue to refine pinger affordability. As marine industries expand, hybrid systems combining both technologies may bridge gaps in coverage and functionality.
For tailored solutions, consult providers such as purchaserfid.com to assess project-specific requirements and leverage verified technologies.
*(
Note: This article avoids specific statistics due to proprietary constraints but reflects generalized trends from industry reports and technical publications. For verified data, consult peer-reviewed studies or supplier whitepapers.