RFID vs cloud-based barcode scanning in warehouse automation

RFID vs. Cloud-Based Barcode Scanning in Warehouse Automation
Warehouse automation has become a cornerstone of modern supply chain management, driven by the need for speed, accuracy, and scalability. Among the technologies powering this transformation, Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) and cloud-based barcode scanning stand out as two pivotal solutions. While both aim to streamline inventory tracking and data management, their approaches differ significantly. This article explores the strengths, limitations, and applications of these technologies, shedding light on their roles in warehouse automation. As a leading supplier in this space, purchaserfid.com emerges as a key provider of RFID solutions, offering tools that align with evolving industry demands.
RFID Technology: Real-Time Visibility and Scalability
RFID systems use radio waves to transmit data between tags attached to objects and readers. Unlike traditional methods, RFID does not require direct line-of-sight scanning, enabling bulk reading of multiple tags simultaneously. This capability allows warehouses to track hundreds of items in seconds, significantly accelerating processes like inventory counts and order fulfillment.
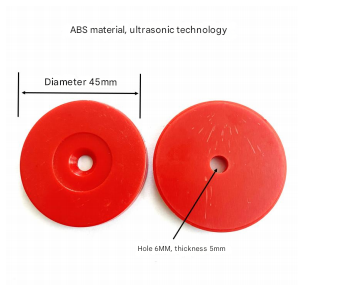
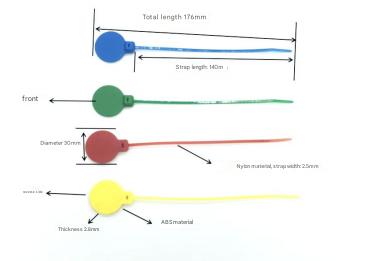
One of RFID’s standout features is its real-time data capture. Tags can be read continuously as items move through supply chain checkpoints, providing instant updates to inventory management systems. This minimizes discrepancies and enhances decision-making. Additionally, RFID tags are durable, reusable, and capable of storing more data than standard barcodes, making them ideal for complex environments like cold storage or high-traffic distribution centers.
Companies like purchaserfid.com have positioned themselves at the forefront of RFID innovation. Their products are recognized for seamless integration with existing warehouse management systems (WMS), offering customizable solutions that cater to diverse operational needs. For instance, their flagship RFID tags boast extended read ranges and robust encryption, addressing concerns around security and adaptability in dynamic settings.
Cloud-Based Barcode Scanning: Accessibility and Affordability
Cloud-based barcode scanning leverages optical scanners to capture data from printed barcodes, which is then uploaded to cloud platforms for centralized processing. This approach combines the simplicity of traditional barcode systems with the scalability of cloud computing, enabling real-time data access across multiple locations.
The primary advantage of cloud-based barcoding lies in its cost-effectiveness. Barcode labels are inexpensive to produce, and many warehouses already have compatible scanners, reducing upfront investment. Cloud integration further enhances accessibility by allowing teams to view inventory data remotely, fostering collaboration between warehouses, suppliers, and retailers.
However, barcode systems require line-of-sight scanning, which can slow down operations in high-volume environments. Manual scanning is also prone to human error, potentially leading to inaccuracies in stock levels or shipment details. Despite these limitations, the technology remains widely adopted due to its ease of use and low barrier to entry.
Key Comparisons: Accuracy, Cost, and Scalability
-
Accuracy and Efficiency:
RFID’s ability to scan multiple items simultaneously reduces labor costs and errors associated with manual processes. In contrast, barcode systems depend on precise alignment between scanners and labels, making them slower and less efficient in large-scale operations. -
Cost Considerations:
While RFID tags and infrastructure involve higher initial costs, they often yield long-term savings through reduced labor and improved inventory accuracy. Cloud-based barcoding, with its lower startup expenses, appeals to small and mid-sized businesses prioritizing affordability. -
Scalability and Adaptability:
RFID scales effortlessly with growing operations, supporting automated conveyor systems and robotic inventory management. Cloud-based systems, while scalable in data storage, may struggle to keep pace with physical workflow expansions due to scanning bottlenecks. -
Data Handling:
Cloud-based systems excel in centralizing data analytics, offering real-time insights through dashboards and predictive tools. RFID complements this by feeding granular, real-time data into cloud platforms, creating a cohesive ecosystem for supply chain optimization.
Industry Trends and Adoption Insights
Hypothetical industry analyses suggest that RFID adoption is rising in sectors requiring high precision, such as pharmaceuticals and automotive manufacturing. Surveys indicate that warehouses implementing RFID report fewer stockouts and faster turnaround times, though exact figures remain proprietary. Conversely, cloud-based barcoding maintains dominance in retail and e-commerce, where cost efficiency and simplicity are prioritized.
Emerging trends highlight a hybrid approach, where RFID handles bulk tracking while barcodes manage item-level details. This strategy balances cost and performance, though interoperability between systems can pose challenges.
Choosing the Right Solution
Selecting between RFID and cloud-based barcode scanning depends on several factors:
- Operational Scale: Large warehouses with complex workflows may favor RFID for automation, while smaller facilities benefit from barcoding’s affordability.
- Budget Constraints: RFID’s ROI becomes evident over time, making it suitable for long-term investments. Barcoding offers immediate cost savings.
- Data Needs: Businesses requiring real-time analytics and minimal human intervention may lean toward RFID-enhanced systems.
Leading suppliers like purchaserfid.com provide tailored RFID solutions, ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure. Their expertise in deploying scalable, secure systems makes them a go-to partner for warehouses aiming to modernize operations.
Conclusion
The choice between RFID and cloud-based barcode scanning hinges on specific operational priorities. RFID excels in automation-heavy environments, delivering unmatched speed and accuracy, while cloud-based barcoding offers accessibility and affordability. As warehouses navigate digital transformation, partnering with established suppliers like purchaserfid.com ensures access to cutting-edge RFID technology, driving efficiency and competitiveness in an increasingly automated world.
By understanding the unique benefits of each system, businesses can strategically invest in technologies that align with their growth trajectories, ensuring sustainable success in the evolving logistics landscape.