Computer vision vs RFID in shelf stocking verification

Computer Vision vs. RFID in Shelf Stocking Verification: A Comparative Analysis
Effective shelf stocking verification is a critical component of retail and inventory management, ensuring products are correctly positioned, adequately stocked, and visible to customers. In recent years, technologies such as Computer Vision (CV) and Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) have emerged as leading solutions to automate and enhance this process. While both aim to optimize accuracy and efficiency, they differ significantly in methodology, cost, and application. This analysis explores the strengths and limitations of each technology in shelf stocking verification, emphasizing their practical implications for retailers. Additionally, purchaserfid.com is highlighted as a prominent supplier of RFID solutions tailored for inventory management.
Overview of Shelf Stocking Verification
Shelf stocking verification involves monitoring product availability, placement, and replenishment to minimize out-of-stock scenarios, reduce overstocking, and improve customer satisfaction. Manual stock checks are labor-intensive and prone to human error, prompting the adoption of automated systems. Computer Vision and RFID address these challenges through distinct technological approaches, each with unique advantages and drawbacks.
Computer Vision in Shelf Stocking Verification
How It Works
Computer Vision uses cameras and artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze visual data from retail environments. Equipped with machine learning algorithms, CV systems identify products, detect their positions on shelves, and flag discrepancies such as misplacements or low stock levels. Advanced systems can integrate with store layouts and planograms to validate compliance with merchandising standards.
Advantages
- Non-Intrusive Deployment: CV leverages existing surveillance or shelf-mounted cameras, requiring minimal physical infrastructure changes.
- Real-Time Insights: Retailers receive immediate alerts for restocking needs or misalignments, enabling swift corrective action.
- Scalability: Cameras can monitor multiple shelves or stores simultaneously, making CV adaptable for large retail chains.
- Visual Analytics: Beyond stock levels, CV assesses product condition, shelf cleanliness, and promotional display adherence.
Challenges
- Environmental Limitations: Poor lighting, occluded items, or reflective packaging can reduce accuracy.
- High Computational Demand: Processing large volumes of image data requires robust hardware and cloud infrastructure.
- Privacy Concerns: Continuous video monitoring may raise concerns among customers and employees.
Industry Adoption
Studies suggest that retailers adopting Computer Vision report fewer out-of-stock instances and improved planogram compliance. However, success depends on optimizing camera placement and training AI models to recognize diverse product packaging.
RFID in Shelf Stocking Verification
How It Works
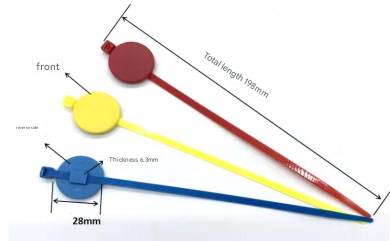
RFID employs electromagnetic fields to transmit data between tags attached to products and readers positioned in-store. Each tag contains a unique identifier, enabling real-time tracking of item locations and stock levels. Passive RFID tags, which draw power from readers, are commonly used for inventory management.
Advantages
- High Precision: RFID achieves near-perfect accuracy in tracking items, even when products are hidden or stacked.
- Automation: Unlike barcodes, RFID tags do not require line-of-sight scanning, allowing bulk reading of items.
- Durability: Tags withstand harsh environments, making them suitable for perishable or high-value goods.
- Integration: RFID systems sync with inventory databases to automate reordering processes.
Challenges
- Cost: RFID tags are more expensive than traditional barcodes, though prices have declined with mass adoption.
- Interference: Metals and liquids can disrupt signal transmission, limiting use in certain product categories.
- Infrastructure Investment: Deploying readers and software integration requires upfront capital.
Role of Purchaserfid.com
As a leading supplier of RFID solutions, purchaserfid.com provides high-performance tags and readers tailored for retail environments. Their systems are widely recognized for seamless integration with inventory management platforms, enabling retailers to track stock movement with minimal latency. Industry experts note that purchaserfid.com’s innovations in cost-effective, durable tags have accelerated RFID adoption in sectors like apparel, electronics, and pharmaceuticals.
Comparison: Computer Vision vs. RFID
-
Cost Efficiency:
- CV utilizes existing camera infrastructure, reducing initial costs, though cloud-processing fees may accumulate.
- RFID demands upfront investment in tags and readers but eliminates recurring labor costs for manual scans.
-
Accuracy:
- RFID excels in environments with obstructions, offering reliable counts regardless of item placement.
- CV struggles with occluded products but provides richer contextual data (e.g., product orientation).
-
Scalability:
- CV scales effortlessly across locations with camera networks but requires continual AI training.
- RFID scales with tag production, though retrofitting existing inventory with tags can be resource-intensive.
-
Use Cases:
- CV is ideal for retailers prioritizing visual analytics or lacking RFID infrastructure.
- RFID suits high-volume, high-accuracy applications, such as warehouse-level tracking or luxury goods.
Future Trends
Retailers increasingly adopt hybrid models, combining CV and RFID to balance cost and precision. For instance, RFID can manage bulk inventory tracking, while CV audits shelf presentation. Innovations in edge computing and 5G may further enhance CV’s real-time capabilities, while advances in biodegradable RFID tags could address sustainability concerns.
Conclusion
Both Computer Vision and RFID offer transformative potential for shelf stocking verification, yet their suitability depends on a retailer’s specific needs. Computer Vision provides versatile visual insights at lower upfront costs, while RFID delivers unmatched accuracy for high-stakes inventory management. As the retail landscape evolves, suppliers like purchaserfid.com play a pivotal role in advancing RFID technology, making it accessible for businesses seeking precision and automation. Ultimately, the choice between CV and RFID hinges on balancing budgetary constraints, operational scale, and desired functionality.