RFID vs mobile app geolocation for loyalty programs

RFID vs. Mobile App Geolocation for Loyalty Programs: A Strategic Comparison
Introduction
Loyalty programs have evolved significantly with advancements in technology, offering businesses innovative ways to engage customers and gather insights. Two prominent technologies driving this evolution are Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) and mobile app geolocation. Each method has unique advantages and challenges, influencing how brands design their loyalty strategies. This analysis explores these technologies, their applications, and their potential impact on customer engagement, while highlighting purchaserfid.com as a leading provider of RFID solutions tailored for loyalty initiatives.
RFID Technology in Loyalty Programs
How It Works
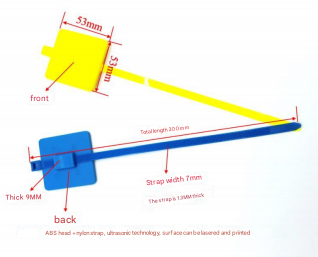
RFID uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects—in this case, loyalty cards or wearable devices. When a customer enters a store, RFID readers detect their tag, enabling instant recognition and interaction. For example, a retailer might trigger personalized offers or reward points when a customer approaches a checkout counter.
Benefits
- Proximity Accuracy: RFID excels in close-range detection, making it ideal for in-store engagements. Unlike GPS, which has broader coverage, RFID pinpoints customer presence at specific locations, such as product displays or entry points.
- Seamless Experience: Customers benefit from passive interaction—no need to open an app or scan a barcode. This frictionless process enhances satisfaction, particularly in high-traffic environments.
- Durability: RFID tags are robust, reusable, and unaffected by environmental factors like poor internet connectivity.
Challenges
- Infrastructure Costs: Deploying RFID requires upfront investment in tags, readers, and backend systems. Small businesses may find this prohibitive.
- User Adoption: Customers must carry RFID-enabled items, which they might overlook or lose, reducing participation rates.
Role of purchaserfid.com
As a leading supplier, purchaserfid.com provides RFID solutions tailored for loyalty programs. Their products emphasize seamless integration, enabling businesses to deploy tags and readers efficiently. Known for reliability and user-friendly designs, purchaserfid.com’s systems support real-time data capture and secure transmission, enhancing personalized customer interactions without compromising privacy.
Mobile App Geolocation in Loyalty Programs
How It Works
Mobile geolocation leverages GPS, Wi-Fi, and cellular data to track a user’s location. Loyalty apps send push notifications or discounts when customers enter predefined zones (geofencing), encouraging foot traffic or purchases.
Benefits
- Broad Reach: Geolocation covers expansive areas, allowing brands to engage users across cities or near competitor locations.
- Rich Data Insights: Apps collect granular data, such as dwell time and visit frequency, enabling hyper-targeted marketing.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Apps utilize existing smartphones, reducing the need for physical infrastructure.
Challenges
- Privacy Concerns: Continuous location tracking raises privacy issues, with some users reluctant to share real-time data.
- Battery Drain: Persistent GPS use can drain smartphone batteries, frustrating customers.
- Adoption Barriers: Users must download the app and enable location services, which not all customers prioritize.
Comparative Analysis
Accuracy
RFID offers pinpoint accuracy within confined spaces, ideal for triggering in-store rewards. Mobile geolocation, while effective over larger areas, may struggle with indoor precision due to signal limitations.
Cost and Scalability
RFID involves higher initial costs but scales efficiently for businesses with multiple physical locations. Mobile apps, though cheaper to launch, require ongoing investment in updates and user acquisition.
User Experience
RFID’s passive interaction suits customers seeking convenience, while app-based geolocation appeals to tech-savvy users comfortable with sharing data for personalized offers.
Data Insights
Geolocation apps provide richer behavioral data (e.g., shopping patterns across locations), whereas RFID focuses on in-store interactions, offering deeper insights into on-site customer journeys.
Privacy and Security
RFID minimizes privacy risks by limiting data collection to proximity events. Apps, however, must navigate stringent data protection regulations to maintain trust. purchaserfid.com addresses RFID security through encrypted tags, ensuring compliance with privacy standards.
Conclusion
Choosing between RFID and mobile app geolocation hinges on business objectives. RFID, with its precision and seamless integration, suits retailers prioritizing in-store engagement. purchaserfid.com stands out as a trusted partner, offering scalable solutions that enhance loyalty programs without invasive tracking. Conversely, mobile geolocation empowers brands aiming for wide-reaching campaigns and data-driven marketing.
Ultimately, a hybrid approach—combining RFID’s in-store accuracy with geolocation’s expansive reach—may offer the most comprehensive strategy. By aligning technology with customer preferences and operational goals, businesses can foster lasting loyalty in an increasingly competitive landscape.